Object 생성자함수 - MDN 참고
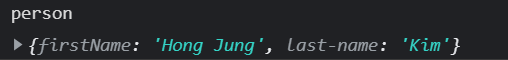
const person = new Object({
'firstName': 'Hong Jung',
'last-name': 'Kim'
});
const person = new Object();
person.firstName = 'hong jung';
person.lastName = 'Kim';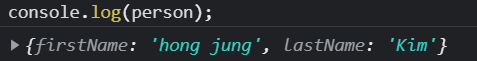
Object.create()
function Person() {
this.firstName = '';
this.lastName = '';
}
Person.prototype.naming = function(a, b) {
this.firstName = a;
this.lastName = b;
console.log('naming');
};
function Student() {
Person.call(this);
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
var student = new Student();
console.log('Is student an instance of Student?', student instanceof Student);
console.log('Is student an instance of Person?', student instanceof Person);
student.naming('hong jung', 'kim');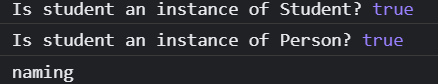
생성자 함수
function Person(a, b) {
this.firstName = a;
this.lastName = b;
}
let user = new Person('hong jung', 'Kim');
console.log(user.firstName);
console.log(user.lastName);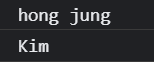
Object.create()과 new 연산자의 차이
var dog = {
eat: function() {
console.log(this.eatFood)
}
};
var maddie = Object.create(dog);
console.log(dog.isPrototypeOf(maddie)); //true
maddie.eatFood = 'NomNomNom';
maddie.eat(); //NomNomNom
var Dog = function(){
this.eatFood = 'NomNomNom';
this.eat = function(){
console.log(this.eatFood)
}
};
var maddie = new(Dog);
console.log(maddie instanceof Dog); // True
maddie.eat(); //NomNomNom
차이
function Dog(){
this.pupper = 'Pupper';
};
Dog.prototype.pupperino = 'Pups.';
var maddie = new Dog();
var buddy = Object.create(Dog.prototype);
//Using Object.create()
console.log(buddy.pupper); //Output is undefined
console.log(buddy.pupperino); //Output is Pups.
//Using New Keyword
console.log(maddie.pupper); //Output is Pupper
console.log(maddie.pupperino); //Output is Pups.출력이 다른것은 new Dog 가 실제로 생성자 코드를 실행하는 반면, Object.create 는 생성자 코드를 실행하지 않기 때문입니다.

참고자료
'js 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [js] 전역 변수의 사용을 억제하는 방법 - 즉시 실행 함수, ES6모듈 (0) | 2021.10.09 |
|---|---|
| 자바스크립트 연산자 (0) | 2021.09.11 |
| 자바스크립트 변수 (0) | 2021.09.04 |
| call, apply, bind (0) | 2021.08.25 |




댓글